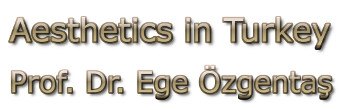Protruding Ears
The ear, which is one of our most important sense organs, has two main parts: 1. The visible part. This is called the outer ear. There is also an invisible part, which is two separate parts: 2a: Middle ear, 2b: Inner ear.
Ear Aesthetics
Most of our facial structures are aesthetically important (eyes, nose, eyebrows, lips). The ear, on the other hand, is considered as secondary in terms of aesthetics, especially in women, since it is under the hair. However, this is not true. As long as the inner and middle ear are intact, the shape of the outer ear, or even its absence, is not a serious obstacle to hearing (with the exceptions of a closed ear hole). However, changes in ear shape are immediately noticeable and aesthetically important.
What is Prominent Ear?
Congenital absence or severe deformity of the ear is included in the group of “congenital disorders” (congenital anomalies) and is rare. On the other hand, the proximity of the auricle to the skull is different for everyone. The fact that the auricle is close to the skull does not attract much attention. On the other hand, it is noteworthy that the scoop is more separated from the skull, that is, it is more prominent when viewed from the front (more area is visible). In society, this image is given derogatory names such as “bat ear”, “sail ear”, “mickey mouse ear”.
Who Is Called Prominent Ears?
We said that the anterior projection of the auricle relative to the skull bones is variable. If this protrusion is more than 2 cm as shown in the picture, prominent ear image has started. The longer this distance, the more noticeable and disturbing the image becomes.
Should prominent ears be treated?
In fact, a prominent ear is not a disease or anomaly. As everyone’s nose size and shape is different, the ear can also have a different appearance. The important thing here is how the person with prominent ears perceives himself. You can see that many adult men and women have prominent ears, and many of these people probably don’t even realize that their ears are protruding forward, or they don’t care. But the situation is different for children. When developing children begin to socialize, that is, when they engage in activities such as going to kindergarten or playing with their neighborhood friends, they examine each other carefully. If they see a difference in one of their friends that they do not have, they ruthlessly criticize him or hir, that is, they humiliate him or hir. Nowadays, it does not attract much attention as it has become commonplace for young children to wear glasses. However, those who have experienced this know very well how their friends treated a primary school child who wore glasses a few decades ago. Growing children are psychologically sensitive. They may not wear glasses when they go to school because they are teased. However, especially boys are not likely to hide their prominent ears, and the taunts of their ruthless friends inflict deep wounds on them. These kids tend to be troublemakers and fight with friends frequently. They don’t want to go to school. Some people urinate on the bed at night (nocturnal enuresis). As soon as the family notices the psychological and social problems related to the prominent ear in the child, they should apply to a “Plastic Reconstructive Surgery” specialist for treatment.
When should a prominent ear be treated?
In fact, a prominent ear can be operated as soon as the child is born. However, it is a known fact that surgeries are more problematic in very young children. It is best to have surgery before the child goes to kindergarten, if possible. The ear is different from other organs in terms of growth. The ear size of a child who has reached the age of 7 is close to 70% of the adult age. For this reason, children with prominent ears can be operated easily at the age of 6-7 years. There is no limit for older patients. Prof. Dr. Ege Özgentaş performed prominent ear surgery on many of his patients over the age of 40. The important thing here is that the person with prominent ears can no longer tolerate the discomfort of this event. This situation can occur at any age, as it occurs in childhood, and necessary surgery is performed.
Prominent Ear Surgery
There is not a single type of surgery accepted all over the world for a prominent ear. There are many treatments described to date. Let’s start with the simplest one:
- Put a bandage on the ears as soon as the baby is born. It is well known that grandmas wear a bandage on newborn babies in a way that tilts the ears back. This treatment has some validity. In newborns, cartilages are under development and this can be permanent when given a certain shape. However, it is difficult to apply an external treatment to newborns. For example, when a bandage is put on the ears, its pressure can cause undesirable changes in the skull bones. Instead, the ears can be shaped by attaching some clips (latches), but this can lead to unwanted marks on the skin. It has been observed that the clamps attached to the ears of rabbit puppies permanently change the shape of the ears in some puppies, but it does not work in some puppies, that is, the ears become erect after a while after the treatment is terminated. The benefit of this method has not yet been proven and is not widely used.
- Operations at school age. These are surgeries that have survived from ancient times and it has become a habit to perform them under general anesthesia in children. Let’s examine these:
- Surgery by incisions made behind the ear. Until recent years, surgery performed by making an incision on the back of the ear was the only option. Here, both the skin was removed from behind the ear and operations were performed to bend the cartilages back. The purpose of removing skin from behind the ear was to stretch the skin here and tilt the ear back. Although it was more difficult to work behind the ear, the lack of suture marks increased the interest in them. The skin removed in the operations performed behind the ear reduces the depth behind the ear and makes it difficult for some to wear glasses.
- Surgery performed by cutting in front of the ear. Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic surgeons need ear cartilages for various corrections and they usually take these cartilages through incisions they make in front of the ear. It is well known that when done properly, there is almost no scar in surgeries performed in this way. This fact has led to an increase in prominent ear surgeries performed by cutting in front of the ear. It is much easier to give the desired shape to the cartilages in operations performed in front of the ear, and the success rate of the operations is significantly higher.
How Does Prof. Özgentaş Operate the Prominent Ears?
Like all physicians, Prof. Dr. Özgentaş also personalizes these surgeries by making unique changes over time in the already known surgeries he performs. The most common problem in prominent ear surgeries is that the patient does not like the image after the dressings are removed. To solve this problem, the “Interactive Surgery” method has been developed. This surgery must be performed under local anesthesia. The first question that comes to mind is whether ear surgery can be performed under local anesthesia for children. The majority of children operated by Dr. Özgentaş are at the age of 6 and above. Contrary to common belief, children at this age can be operated without any problems if they are properly informed before the operation and a proper local anesthesia is performed with minimal pain. Most of the young children are so disturbed by the image in their ears that they agree to lie on the operating table in order to get a good result, despite their continuing fears. In other words, their psychological pain outweighs the fear of surgery. In fact, the operation is completely painless and the child is relieved when he realizes it. There is no problem with local anesthesia at older ages.
Interactive Operation for Prominent Ear
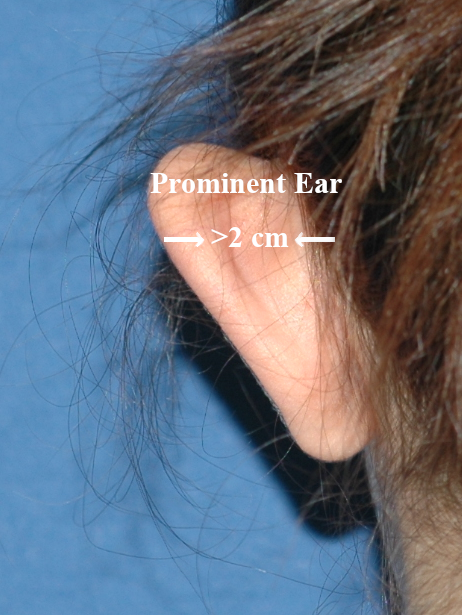
The operation begins by making an incision in front of the ear. Necessary procedures are applied to the ear cartilages and U-shaped sutures are placed in the middle part of the auricle to form an antihelix (to tilt the ear backwards). After these stitches are placed in sufficient numbers, their knots are prepared but not tightened. The patient is placed in a sitting position on the operating table and a mirror is held in front of him to see his face and ears clearly. Dr. Özgentaş gradually begins to tighten the knots of the sutures that tilt the ear back, and as the ear gradually lies back, the patient is asked to warn the doctor when the patient’s happiest or most desired shape emerges. In this way, the knots are tightened or loosened to find the exact shape that the patient wants. After the patient approves the final shape, the nodes are fixed. The patient is laid back on the table, all open parts are sutured and the surgery is finished by wrapping the ears.
Post-Operative Care
A light pressure bandage is applied to the ears for a maximum of 3 days after the surgery. However, in some cases, it is possible to open the bandage with the patient’s desire, even the day after the surgery. After the bandage is opened, a hair (tennis) band is attached to cover only the upper pole of the ear, and it is recommended to use it for at least a month if possible. It is recommended that those who cannot wear a bandage during the day due to their job use this band at least during non-working hours. Post-operative pain is tolerable, and most patients can get relief from pain only by taking paracetamol tablets once or twice a day.
Conclusion
Prominent ear surgeries are included in the group of surgeries that can be performed interactively, that is, where the patient can convey their wishes and comments while the surgery is in progress. In order for this to happen, the operation must be performed with local anesthesia, that is, the patient must be awake. In surgeries performed in this way, patient satisfaction is high and the occurrence of undesirable results after surgery can be minimized.